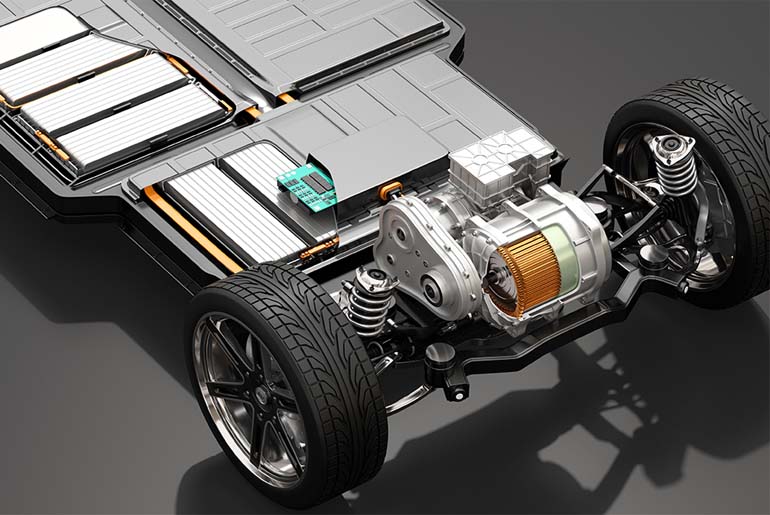
Electric vehicles (EVs) are at the forefront of the automotive industry’s transformation towards sustainability and efficiency. Central to the performance and functionality of EVs are inverters and power electronics, which play a crucial role in the powertrain system. These components ensure that electric vehicles operate efficiently, deliver the required power, and provide a seamless driving experience. This article explores the essential functions of inverters and power electronics in EV powertrains, highlighting their impact on the overall performance and efficiency of electric vehicles.
Understanding Inverters and Power Electronics
Power electronics encompass a range of devices that control and convert electrical power in various forms to meet specific requirements. Inverters, a subset of power electronics, are particularly critical in EVs as they convert direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) to drive the electric motor. The interplay between inverters and other power electronic components ensures the efficient operation of the EV powertrain.
Key Functions of Inverters in EV Powertrains
- DC to AC Conversion: The primary function of an inverter in an EV is to convert the DC power stored in the battery to AC power needed by the electric motor. This conversion is vital because most high-performance electric motors operate on AC power due to its efficiency and suitability for variable speed control.
- Motor Control: Inverters are responsible for controlling the speed and torque of the electric motor. By adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the AC power supplied to the motor, the inverter can precisely regulate the motor’s performance, ensuring smooth acceleration, deceleration, and optimal power delivery.
- Regenerative Braking: Inverters enable regenerative braking, a process where the electric motor functions as a generator during braking, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy and storing it in the battery. This not only improves the efficiency of the vehicle but also extends the driving range by recovering energy that would otherwise be lost as heat.
- Thermal Management: Advanced inverters are equipped with thermal management systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Efficient cooling solutions are essential to prevent overheating, which can degrade performance and reduce the lifespan of electronic components.
Advances in Power Electronics
The development of power electronics has been pivotal in enhancing the performance and efficiency of EV powertrains. Some of the significant advancements include:
- Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors: Traditional silicon-based semiconductors are being increasingly replaced by wide-bandgap materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These materials offer superior electrical properties, including higher efficiency, faster switching speeds, and better thermal performance. SiC and GaN inverters contribute to reduced energy losses, improved efficiency, and more compact designs.
- High-Efficiency Inverters: Modern inverters are designed to maximize efficiency and minimize energy losses. Innovations such as multi-level inverter topologies and advanced pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques help achieve higher efficiency levels. These improvements are crucial for extending the range and performance of EVs.
- Integrated Power Electronics Systems: Integration of various power electronic components into a single, compact module enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of the EV powertrain. Integrated systems reduce the need for separate cooling solutions and interconnects, leading to simpler designs and improved performance.
- Smart Control Algorithms: Advanced control algorithms enable more precise and adaptive management of power electronics. Techniques like field-oriented control (FOC) and direct torque control (DTC) optimize motor performance under varying conditions, ensuring efficient power delivery and enhancing the driving experience.
Impact on EV Performance and Efficiency
The advancements in inverters and power electronics have had a profound impact on the performance, efficiency, and reliability of electric vehicles. Key benefits include:
- Improved Range: Enhanced inverter efficiency and regenerative braking capabilities contribute to extending the driving range of EVs by maximizing energy utilization and recovery.
- Better Performance: Advanced motor control algorithms and high-efficiency inverters provide smoother acceleration, precise torque control, and superior overall vehicle performance.
- Reduced Weight and Size: The use of wide-bandgap semiconductors and integrated power electronics systems leads to more compact and lightweight designs, which further improves vehicle efficiency and handling.
- Increased Reliability: Effective thermal management and robust designs enhance the durability and reliability of power electronic components, ensuring consistent performance over the vehicle’s lifespan.
Future Prospects
The future of inverters and power electronics in EV powertrains is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at further improving efficiency, performance, and integration. Emerging technologies such as solid-state batteries and advanced semiconductor materials will continue to drive innovation in power electronics. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into control systems will enable even more adaptive and efficient management of powertrain components.
Conclusion
Inverters and power electronics are the unsung heroes of EV powertrains, playing a critical role in converting and managing electrical power to ensure optimal vehicle performance. With continuous advancements in semiconductor materials, control algorithms, and integrated systems, the efficiency and capability of EV powertrains are set to reach new heights. These innovations not only enhance the driving experience but also contribute to the broader goal of sustainable and eco-friendly transportation.