 Adverse environmental impact of petroleum-based transportation has been the key motivator for the development of advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and their popularity.
Adverse environmental impact of petroleum-based transportation has been the key motivator for the development of advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and their popularity.
Emerging as a recognized solution to counter the carbon emissions generated by ICE-based engines, Electric Vehicles (EVs) are expected to retain their position as one of the preferred choices for transition to clean energy-based fuel.
Widely accepted as one of the advanced technologies which shows economic feasibility, EVs provides their users with enhanced efficiency through improved fuel economy along with reduced emissions.
Aside from this, the advent of electric vehicles is expected to offer a diversity of fuel-based options for clean transportation.
Required to have a range of advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) to support their production and performance, the growth of various Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) focused on manufacturing EV-based materials is rising day by day.
Keeping these points in mind, OEMs have picked some of the most efficient Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) that can enhance their performance to its maximum levels.
Key Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Here are some of the key advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) that are considered for EVs production,
Lightweight Materials
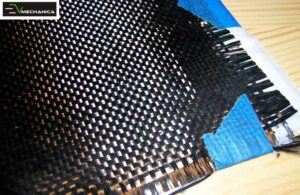 One of the most significant Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) include lightweight materials like aluminum, magnesium, and carbon fiber are essential for improving EVs’ efficiency and performance. For example, Tesla’s Model S uses a high-strength aluminum structure that reduces weight and enhances its range.
One of the most significant Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) include lightweight materials like aluminum, magnesium, and carbon fiber are essential for improving EVs’ efficiency and performance. For example, Tesla’s Model S uses a high-strength aluminum structure that reduces weight and enhances its range.
Carbon fiber is another lightweight and strong material that can help improve the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles. BMW is a company that has been using carbon fiber in its EVs for several years. The BMW i3, for example, features a carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) passenger cell, which reduces the weight of the vehicle and improves its overall efficiency.
High-Energy-Density Batteries
Electric vehicles rely heavily on advanced batteries to store energy and power the electric motor. High-energy density battery technologies like lithium-ion, solid-state, and lithium-sulfur are being developed to increase range and reduce charging times. For instance, Volkswagen is investing in solid-state batteries that offer more significant energy storage and faster charging than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Rare-Earth Metals
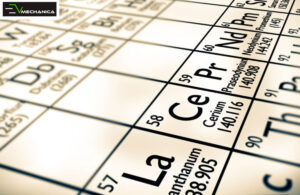 Other vital Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) depend on rare-earth metals like neodymium, dysprosium, and cobalt to produce permanent magnets for electric motors. Companies are working to reduce the use of these expensive and environmentally harmful materials in their EV production.
Other vital Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) depend on rare-earth metals like neodymium, dysprosium, and cobalt to produce permanent magnets for electric motors. Companies are working to reduce the use of these expensive and environmentally harmful materials in their EV production.
For example, BMW is using recycled rare-earth metals to manufacture electric drivetrains. Companies such as Toyota are also working to reduce their reliance on rare earth elements in their EV production. Toyota’s new electric motor design uses fewer rare earth elements than previous versions, which reduces the cost and environmental impact of EV production.
Graphene
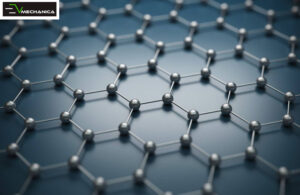 Counted as another advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs), Graphene, a one-atom-thick carbon sheet, has the potential to enhance EV batteries’ performance, energy density, and lifespan. Tesla acquired graphene battery developer Maxwell Technologies in 2019 to advance its battery technology and improve EV performance.
Counted as another advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs), Graphene, a one-atom-thick carbon sheet, has the potential to enhance EV batteries’ performance, energy density, and lifespan. Tesla acquired graphene battery developer Maxwell Technologies in 2019 to advance its battery technology and improve EV performance.
Companies such as Real Graphene are working to develop graphene-based batteries that are more durable and have a longer lifespan than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Materials Considered for Cathode
Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) are closely related to the development of batteries which is one of the primary components. One of the most popular lithium-ion types is lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), lithium manganese oxide (LMO), lithium iron phosphate (LFP), lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA), as well as lithium titanate (LTO).
Generally, batteries based on LMO cathodes employ manganese dioxide (MnO2) as their basic material, with the advantages of employing earth-abundant and non-toxic materials. LiMn2O4 is one of the well-established LMO formulations that includes several different compounds designed to manage the relative drawbacks of LMO ranging from physical degradation due to the dissolution of electrode material.
Sustainable Materials
Sustainable Materials for Electric vehicles (EVs) like bio-based plastics, natural fiber composites, and recycled materials are being used in EV production to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainability. For instance, Ford is developing car parts made from agave fiber and coconut shells to improve sustainability.
Materials for Charger Housing
Key Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) used for housing batteries include patented polycarbonate resins and blends to provide high utility in the manufacturing of charger housing, front covers, light guides, display lenses and connectors for both outdoor as well as indoor charging stations.
Other materials that can be considered include polyurethanes, thermoplastic polyurethanes, and elastomers that are used for the fabrication of decorative parts in connectors and their associated power cables and holders.
Wrapping Up
 In short, advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) like lightweight metals, high-energy-density batteries, rare-earth metals, graphene, and sustainable materials are essential for supporting the production and performance of electric vehicles. These advanced materials are vital in making EVs more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective.
In short, advanced Materials for Electric Vehicles (EVs) like lightweight metals, high-energy-density batteries, rare-earth metals, graphene, and sustainable materials are essential for supporting the production and performance of electric vehicles. These advanced materials are vital in making EVs more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective.
