In March 2024, the White House and the Environmental Protection Agency in the United States unveiled aggressive pollutant emission standards. The regulations targeted gas-powered vehicles, but their agenda is clearly to push for the nationwide adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Officials estimate that nearly 70% of all new car sales will have zero emissions within a few years.
Currently, EVs hold a 7.6% market share in the U.S., but those numbers are rising. EVs constituted 10% of all vehicle sales in the third quarter of last year, highlighting the increased adoption and acceptance of EVs in the automotive industry. The numbers are even more bullish in Europe, where EVs hold a 14.6% market share.
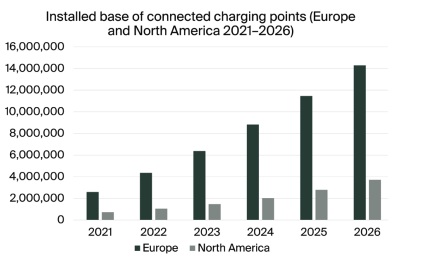
Not surprisingly, the number of connected EV charging points is expected to grow to keep up with the demands of cars on the road. Independent analyst firm Berg Insight predicts that they will reach 18 million in Europe and North America by 2026. Concerns over vehicle emissions and climate change will continue to push the market forward, and all those electric vehicles need charging points to power the electric revolution.
The Importance of Connectivity in EV Charging Infrastructure
Private, semi-private, and public charging stations all need connectivity, although they have different reasons for it. Private charging stations are charging points located on private property. The owner has full control over who can access the charging station. This type of charging station is intended for private use.
Connectivity for these installations is primarily required to connect the station with the charge point operator (CPO). The CPO uses the connectivity to remotely monitor the station. It might also use the connection for software or firmware updates.
Semi-private charging points are located at businesses, shopping centers, hotels, and other similar places. They are reserved for customers, employees, or other specific populations. These points are not open to the general public but might require some type of authentication for use. Public charging points are accessible to anyone. They may be charging points placed along the road, city centers, or public parking lots.
Like private installations, public and semi-private charging points use connectivity with their CPO for maintenance, real-time remote monitoring, and EV chargers site management. It allows them to meter usage, identify customers, and bill accordingly. The real-time data allows them to understand demand. In semi-private locations it also facilitates user authentication.
Connectivity is also in place to benefit drivers. Using an app or website, drivers can discover public and semi-private charging points and ensure that the type of connector at the station is compatible with their vehicle’s system. They can reserve time slots, monitor charging from an app on their phones, and pay for the service.
Leveraging cellular LTE-M: The Ideal Protocol for EV Charging Points
Selecting the right connectivity protocol for EV charging points is paramount to ensuring efficient operation and seamless user experience. Charge point operators have several connectivity options: cellular alternatives such as LTE-M or CAT-1 (or higher categories), Wi-Fi, fixed line, and even more. In this article, we’ll focus on the two LPWA technologies – LTE-M and CAT-1 – due to their wide coverage, robust security, ease of installation, and lower cost of ownership compared to Wi-Fi and Ethernet, which require additional infrastructure and might increase costs significantly, particularly in public chargers stations.
Choosing between LTE-M and CAT-1 should be based on the needs of the application. CAT-1 is often the better option when operations require a higher data rate. However, most EV charging points have low data transmission requirements, and LTE-M should be highly considered.
For global EV charging device manufacturers, one of the most compelling drivers for LTE-M is its support of multiple frequency bands with a single hardware design. This eliminates the need for design variants based on regional or network operator needs.
LTE-M operates on a Half-Duplex Frequency Division Duplex (HD-FDD), enabling simultaneous data transmission and reception. In contrast, CAT-1 technology requires additional hardware components, such as duplexers and filters, to separate the frequencies for each band. As a result, CAT-1 installations have higher hardware costs, reduced flexibility in the early stages of design, and cannot be changed once installed. By using HD-FDD, LTE-M streamlines hardware requirements, lowers costs, and provides a versatile and scalable connectivity solution.
Another key consideration when selecting a network for IoT applications is coverage extension. Some EV charge points will be located deep within garages or in areas of a house with limited connectivity. In these scenarios, LTE-M stands out as an IoT-optimized technology, designed to operate in poor connectivity conditions, ensuring continuous data transfer. CAT-1 and CAT-1bis, on the other hand, might disconnect as conditions deteriorate.
As mobile carriers move to 5G networks, LTE-M becomes a key part of the larger cellular IoT system. Its compatibility with 5G ensures smooth integration and ongoing support for IoT projects. LTE-M’s future-proofing helps businesses like EV charger manufacturers stay ahead in the age of 5G innovation, surpassing the lifespan of older 4G technologies like LTE CAT-1 or CAT-1bis.
The wireless connectivity LTE-M delivers simplifies charge point rollouts, and its ease of deployment makes it the right choice for the EV charging infrastructure. LTE-M enables rapid deployments of charging stations at scale, facilitating the expansion of charging networks to meet the growing demands of EV adoption.
The Evolution of the Charging Infrastructure
In the ever-evolving landscape of EV charging infrastructure, adopting LTE-M as the connectivity protocol for EV Charging Points would mark a significant step forward. This versatile solution addresses the diverse connectivity needs of geographically dispersed charging points. As the world transitions towards a sustainable future, embracing technologies like LTE-M paves the way for a seamless and efficient charging experience, driving the electrification revolution forward.

